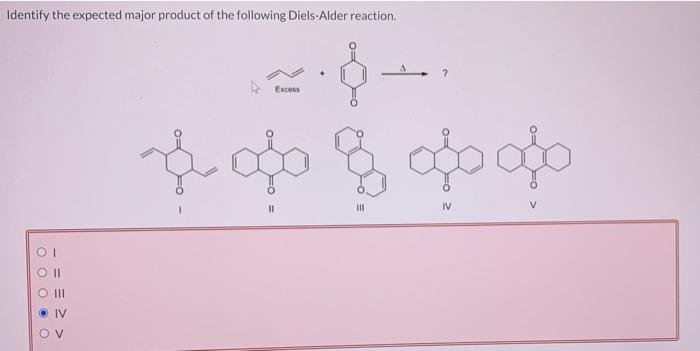
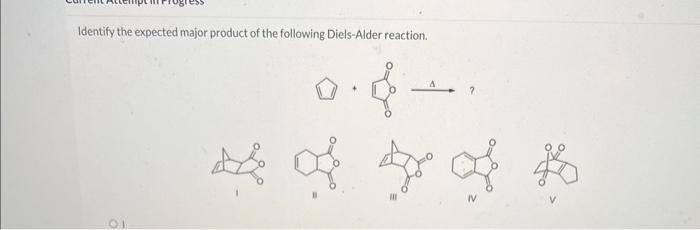
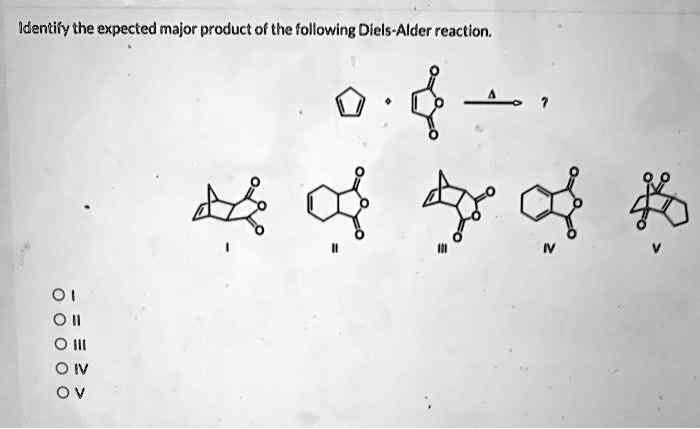
Identify the expected major product of the following diels-alder reaction. – Diels-Alder reactions are powerful tools in organic synthesis, enabling the formation of cyclic compounds with high regio- and stereoselectivity. This article provides an overview of the factors influencing the regio- and stereoselectivity of Diels-Alder reactions and guidelines for predicting the expected major product.
The regio- and stereoselectivity of Diels-Alder reactions are governed by the electronic properties of the diene and dienophile, as well as the reaction conditions. The diene’s HOMO and the dienophile’s LUMO interact in a concerted manner, leading to the formation of a new sigma bond between the diene’s carbons and the dienophile’s carbons.
The regiochemistry of the reaction is determined by the relative reactivity of the diene’s carbons, while the stereochemistry is determined by the relative orientation of the diene and dienophile.
Introduction to the Diels-Alder Reaction
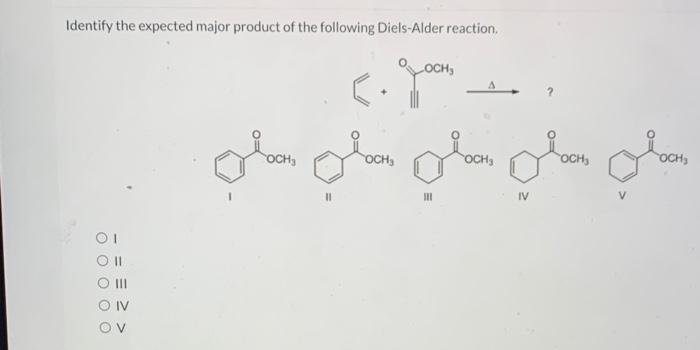
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclic compound. It is a powerful tool in organic synthesis due to its versatility and ability to create complex carbon-carbon bonds.
Identifying the Expected Major Product
The regio- and stereoselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction are influenced by several factors, including:
- Substituents on the diene and dienophile:Electron-withdrawing groups on the diene and electron-donating groups on the dienophile favor the formation of the endo product.
- Steric effects:Bulky substituents on the diene or dienophile can hinder the formation of certain products.
- Solvent effects:Polar solvents favor the formation of the endo product, while nonpolar solvents favor the formation of the exo product.
Examples and Applications
The Diels-Alder reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the construction of various cyclic compounds. Some examples include:
- Synthesis of cyclohexenes:The reaction of 1,3-butadiene with maleic anhydride yields cyclohexene.
- Synthesis of alkaloids:The Diels-Alder reaction is a key step in the synthesis of many alkaloids, such as morphine and strychnine.
- Synthesis of terpenes:The Diels-Alder reaction is used to synthesize terpenes, which are natural products with diverse biological activities.
Advanced Considerations, Identify the expected major product of the following diels-alder reaction.
The use of chiral auxiliaries and catalysts can control the stereoselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction. Chiral auxiliaries are attached to the diene or dienophile to induce asymmetry, while catalysts can accelerate the reaction and improve the yield.
The endo and exo products of the Diels-Alder reaction refer to the relative orientation of the substituents on the newly formed ring. The endo product has the substituents on the same side of the ring, while the exo product has the substituents on opposite sides.
FAQ Explained: Identify The Expected Major Product Of The Following Diels-alder Reaction.
What is the Diels-Alder reaction?
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclohexene ring.
What factors influence the regio- and stereoselectivity of Diels-Alder reactions?
The regio- and stereoselectivity of Diels-Alder reactions are influenced by the electronic properties of the diene and dienophile, as well as the reaction conditions.
How can I predict the expected major product of a Diels-Alder reaction?
The expected major product of a Diels-Alder reaction can be predicted by considering the relative reactivity of the diene’s carbons and the relative orientation of the diene and dienophile.