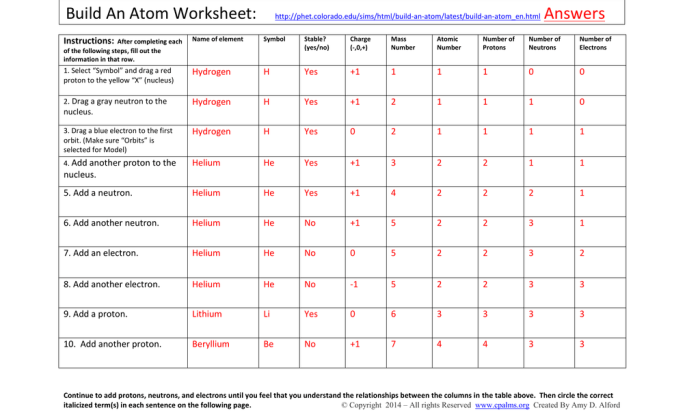
Atomic structure ions and isotopes worksheet answers chemistry corner – Welcome to the realm of atomic structure, ions, and isotopes, where the fundamental building blocks of matter are unveiled. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate details of atoms, their charged counterparts, and their diverse isotopic forms, providing a deep understanding of the very essence of our physical world.
Our journey begins with an exploration of atomic structure, where we uncover the fundamental components of atoms—protons, neutrons, and electrons—and their pivotal roles in shaping the properties of matter. We then venture into the fascinating realm of ions, examining how atoms gain or lose electrons to acquire an electrical charge.
Finally, we delve into the world of isotopes, exploring their unique characteristics and their indispensable applications in various scientific fields.
Atomic Structure: Atomic Structure Ions And Isotopes Worksheet Answers Chemistry Corner
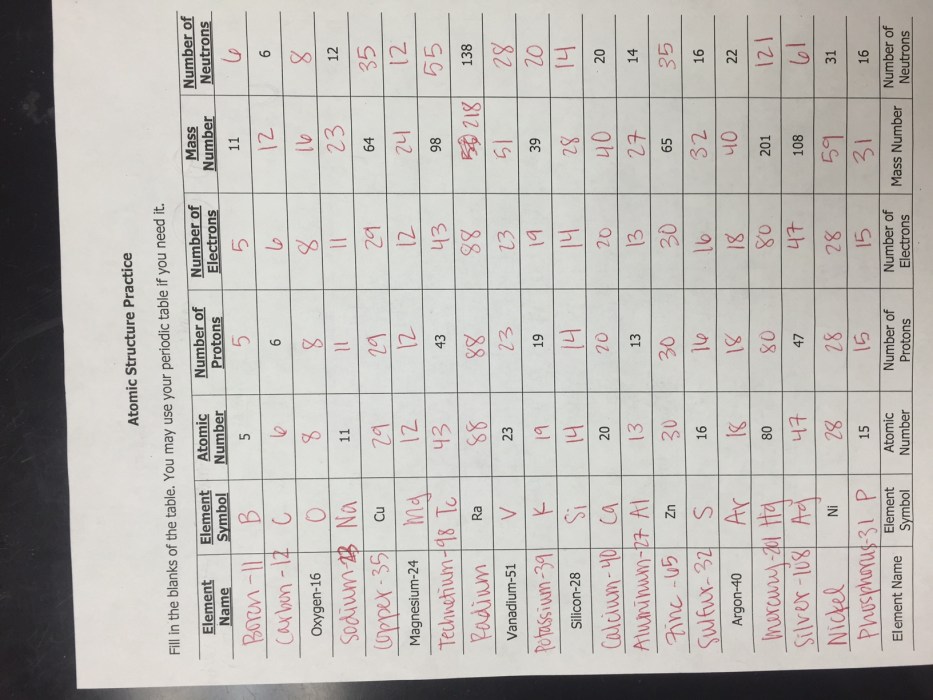
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a central nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons, which have a positive charge, and neutrons, which have no charge.
The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element to which the atom belongs. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus is equal to the number of protons, giving the atom a neutral charge. The mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus, with protons and neutrons contributing almost equally to the mass.

Role of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Protons: Determine the element and contribute to the mass of the atom.
- Neutrons: Contribute to the mass of the atom and affect its stability.
- Electrons: Surround the nucleus, have a negative charge, and determine the chemical properties of the atom.
Ions
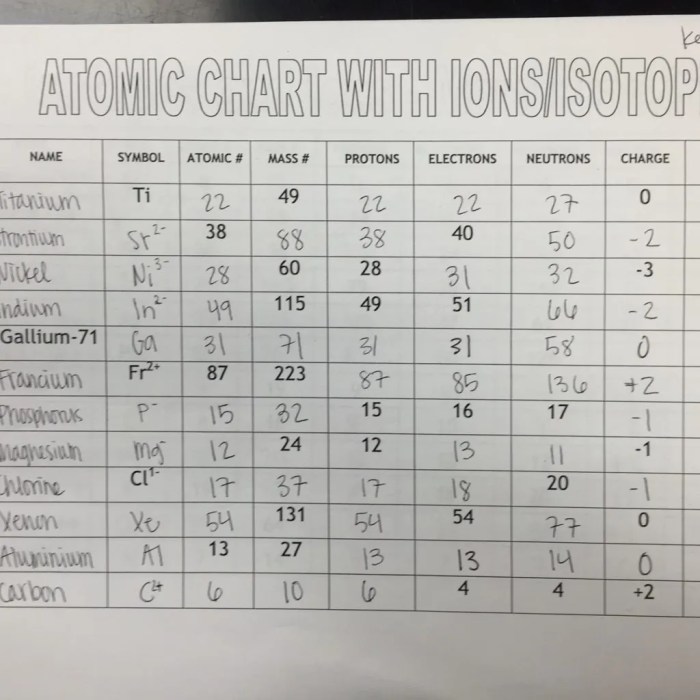
An ion is an atom or molecule that has lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion called a cation. When an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion.
Types of Ions, Atomic structure ions and isotopes worksheet answers chemistry corner
- Cations: Positively charged ions formed by losing electrons.
- Anions: Negatively charged ions formed by gaining electrons.
Common Ions and Their Charges
| Ion | Charge | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium ion | +1 | Na+ |
| Chloride ion | -1 | Cl– |
| Calcium ion | +2 | Ca2+ |
| Sulfate ion | -2 | SO42- |
Isotopes
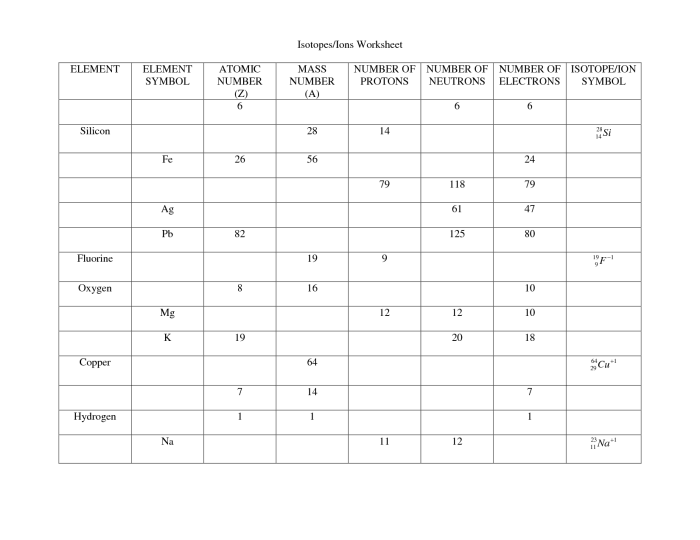
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This results in different masses for the isotopes.
Radioactive Isotopes
Some isotopes are radioactive, meaning they undergo spontaneous decay by emitting particles or energy. This decay can be used in applications such as:
- Medical imaging and treatment
- Radioactive dating
- Industrial tracing
Examples of Isotopes and Their Uses
| Isotope | Mass Number | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 12 | Standard for atomic mass |
| Carbon-14 | 14 | Radioactive dating |
| Uranium-235 | 235 | Nuclear fuel |
| Iodine-131 | 131 | Medical imaging and treatment |
Question Bank
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
An atom is a neutral entity with an equal number of protons and electrons, while an ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.
How do isotopes differ from each other?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different neutron numbers, leading to variations in their mass and certain properties.
What are the applications of radioactive isotopes?
Radioactive isotopes find diverse applications in medicine, such as cancer treatment and medical imaging, as well as in scientific research and industrial processes.