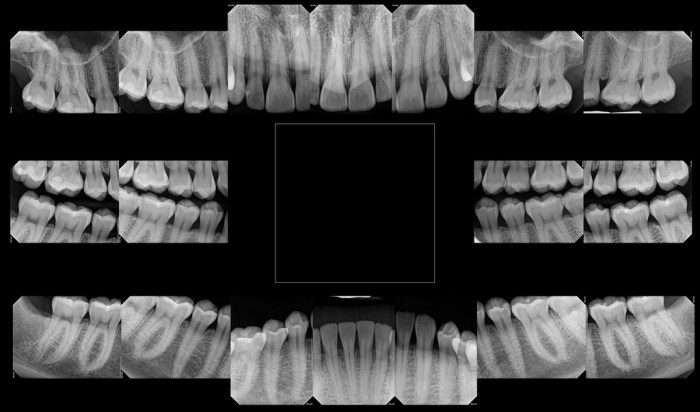
Scanning of traditional film-based radiographs into a digital image – The digitization of traditional film-based radiographs into digital images has revolutionized medical imaging, offering a plethora of advantages and opening new avenues for clinical practice. This comprehensive guide delves into the process, techniques, and applications of this transformative technology, providing a comprehensive overview for healthcare professionals and researchers.
By converting analog radiographs into digital formats, healthcare providers can leverage the benefits of improved image quality, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and seamless data management. This guide explores the equipment and techniques used in the digitization process, highlighting the importance of calibration and maintenance for optimal image quality.
Digitalization of Film-Based Radiographs: Scanning Of Traditional Film-based Radiographs Into A Digital Image
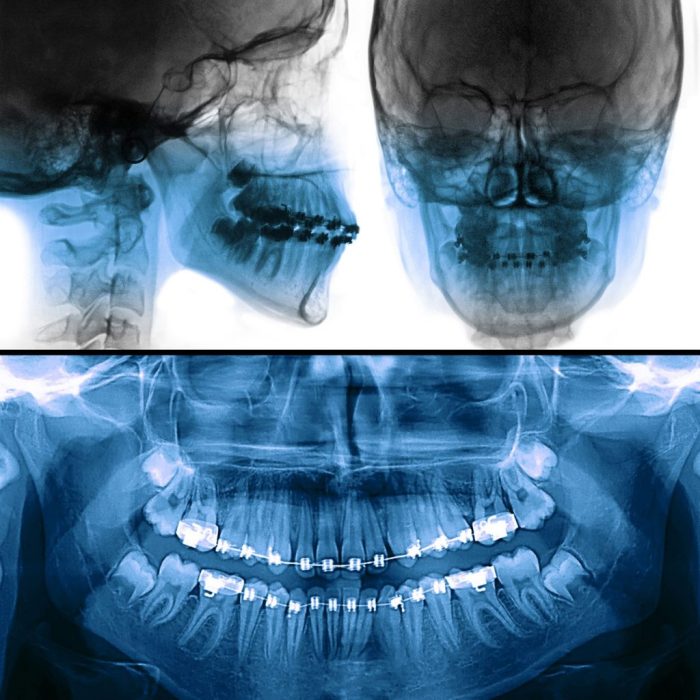
The digitization of film-based radiographs involves converting traditional film-based radiographs into digital images using specialized scanners. This process offers several advantages, including improved image quality, ease of storage, and enhanced accessibility.
By converting film-based radiographs into digital images, healthcare providers can take advantage of the benefits of digital technology. These benefits include the ability to store and retrieve images electronically, the ability to share images with other providers, and the ability to manipulate and enhance images to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Equipment and Techniques
The digitization of film-based radiographs requires specialized scanners designed to capture the images from the film. These scanners typically use a combination of light sources and sensors to create a digital representation of the radiograph.
There are two main types of scanners used for digitizing film-based radiographs: flatbed scanners and drum scanners. Flatbed scanners are designed to scan flat film-based radiographs, while drum scanners are designed to scan curved film-based radiographs.
The scanning technique used will impact the quality of the digital image. The resolution of the scanner, the type of light source used, and the scanning speed can all affect the quality of the digital image.
Image Processing and Enhancement, Scanning of traditional film-based radiographs into a digital image
Once the film-based radiograph has been digitized, image processing techniques can be used to enhance the quality of the image. These techniques can be used to improve the contrast, brightness, and sharpness of the image.
There are a variety of software tools available for image processing. These tools can be used to perform a variety of tasks, such as cropping, rotating, and resizing images.
Image processing can be used to improve the diagnostic accuracy of radiographs. By enhancing the contrast and brightness of the image, it can be easier to see small details that may have been missed on the original film-based radiograph.
Data Management and Storage
The digitization of film-based radiographs creates large volumes of digital images that need to be managed and stored. This can be a challenge for healthcare providers, as they need to ensure that the images are stored securely and that they can be easily accessed when needed.
There are a variety of storage options available for digital radiographic images. These options include Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), cloud storage, and optical disc storage.
PACS is a specialized software system that is designed to store and manage digital radiographic images. PACS systems allow healthcare providers to store, retrieve, and view images from a central location.
Clinical Applications
The digitization of film-based radiographs has had a significant impact on clinical practice. Digital radiographs are now used in a wide variety of clinical settings, including:
- Diagnostic imaging
- Teleradiology
- Remote consultations
- Research and education
Digital radiographs offer several advantages over traditional film-based radiographs. Digital radiographs are more convenient to store and retrieve, they can be shared more easily with other providers, and they can be manipulated and enhanced to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Future Trends
The field of digital radiography is constantly evolving. New technologies and advancements are emerging all the time, and these advancements are having a significant impact on the way that radiographs are used in clinical practice.
One of the most promising trends in digital radiography is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to analyze and interpret digital radiographs, and this can help to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
As AI continues to develop, it is likely that it will play an increasingly important role in the field of digital radiography. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way that radiographs are used in clinical practice, and it could lead to new and innovative ways to diagnose and treat diseases.
General Inquiries
What are the key advantages of digitizing film-based radiographs?
Digitization offers numerous advantages, including improved image quality, reduced storage space requirements, enhanced accessibility, and easier image sharing and collaboration.
What types of scanners are used for digitizing radiographs?
There are various types of scanners used, including flatbed scanners, drum scanners, and computed radiography (CR) systems. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for different applications.
How can image processing techniques enhance the quality of digitized radiographs?
Image processing techniques such as contrast enhancement, noise reduction, and edge detection can significantly improve the visibility and diagnostic value of digitized radiographs.
What are the challenges associated with managing and storing large volumes of digital radiographic images?
Managing and storing large volumes of digital radiographic images requires robust data management systems, such as PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), to ensure efficient storage, retrieval, and data security.
How is digital radiography transforming clinical practice?
Digital radiography has revolutionized clinical practice by enabling teleradiology, remote consultations, and the integration of medical images into electronic health records, leading to improved patient care and enhanced collaboration among healthcare professionals.