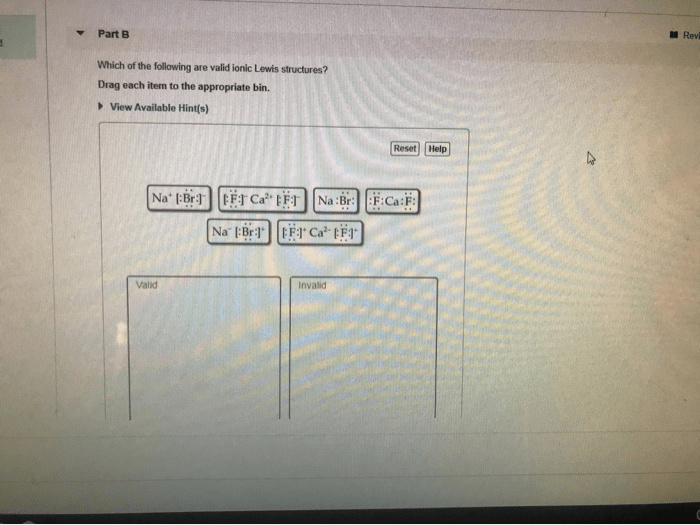
Which of the following are valid ionic Lewis structures? This question delves into the realm of chemical bonding, exploring the fundamental principles that govern the formation and stability of ionic compounds. By examining the characteristics and properties of valid ionic Lewis structures, we gain insights into the behavior and interactions of ions, providing a deeper understanding of the molecular world.
Ionic Lewis structures serve as visual representations of ionic compounds, depicting the arrangement of ions and their respective charges. Understanding the criteria for valid ionic Lewis structures is crucial for accurately predicting the properties and reactivity of these compounds. This exploration will shed light on the factors that determine the validity of ionic Lewis structures, guiding us towards a comprehensive understanding of ionic bonding.
Ionic Lewis Structures
Ionic Lewis structures are a type of chemical notation that represents the bonding between ions in an ionic compound. They show the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that gives up electrons becomes a positively charged ion (cation), while the atom that receives electrons becomes a negatively charged ion (anion). The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.
Identifying Valid Ionic Lewis Structures, Which of the following are valid ionic lewis structures
To determine if an ionic Lewis structure is valid, the following criteria must be met:
- The total charge of the ions must be zero.
- The ions must have the correct oxidation states.
- The ions must be arranged in a way that minimizes electrostatic repulsion.
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more likely it is to gain electrons and become an anion. Oxidation state is a measure of the charge of an atom in a compound.
It is determined by the number of electrons that the atom has gained or lost.
Examples of Valid and Invalid Ionic Lewis Structures
| Valid | Invalid |
|---|---|
| Na+ Cl– | Na– Cl+ |
| Mg2+ O2- | Mg+ O– |
| Al3+ F– | Al2+ F2- |
The valid ionic Lewis structures are valid because they meet the criteria listed above. The total charge of the ions is zero, the ions have the correct oxidation states, and the ions are arranged in a way that minimizes electrostatic repulsion.
The invalid ionic Lewis structures are invalid because they do not meet the criteria listed above. The total charge of the ions is not zero, the ions do not have the correct oxidation states, or the ions are not arranged in a way that minimizes electrostatic repulsion.
Common Errors in Drawing Ionic Lewis Structures
Some common errors that students make when drawing ionic Lewis structures include:
- Forgetting to include the charges on the ions.
- Drawing the ions with the wrong oxidation states.
- Arranging the ions in a way that does not minimize electrostatic repulsion.
To avoid these errors, it is important to remember the criteria for valid ionic Lewis structures and to practice drawing them.
Applications of Ionic Lewis Structures
Ionic Lewis structures are used in a variety of applications in chemistry. They can be used to:
- Predict the properties of ionic compounds.
- Explain the behavior of ionic compounds in solution.
- Design new ionic compounds with desired properties.
Ionic Lewis structures are a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of ionic compounds.
FAQ Guide: Which Of The Following Are Valid Ionic Lewis Structures
What is an ionic Lewis structure?
An ionic Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the arrangement of ions in an ionic compound, showing the transfer of electrons between atoms to form charged species.
How do I determine if an ionic Lewis structure is valid?
To determine if an ionic Lewis structure is valid, check if the following criteria are met:
- The total charge of the ions adds up to zero.
- The ions have the correct oxidation states.
- The ions are arranged in a stable configuration.
What are some common errors in drawing ionic Lewis structures?
Common errors include:
- Incorrectly assigning oxidation states.
- Not balancing the charges of the ions.
- Drawing ions with incorrect electron configurations.