Introducing the answer key to protein synthesis worksheet, an indispensable tool for understanding the intricate process of protein synthesis. This comprehensive guide unveils the central dogma of molecular biology, illuminating the roles of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomes in this fundamental biological mechanism.
Delve into the processes of transcription and translation, exploring the structure and function of RNA polymerase and ribosomes. Witness the formation of mRNA and polypeptide chains, unraveling the genetic code that governs the synthesis of proteins.
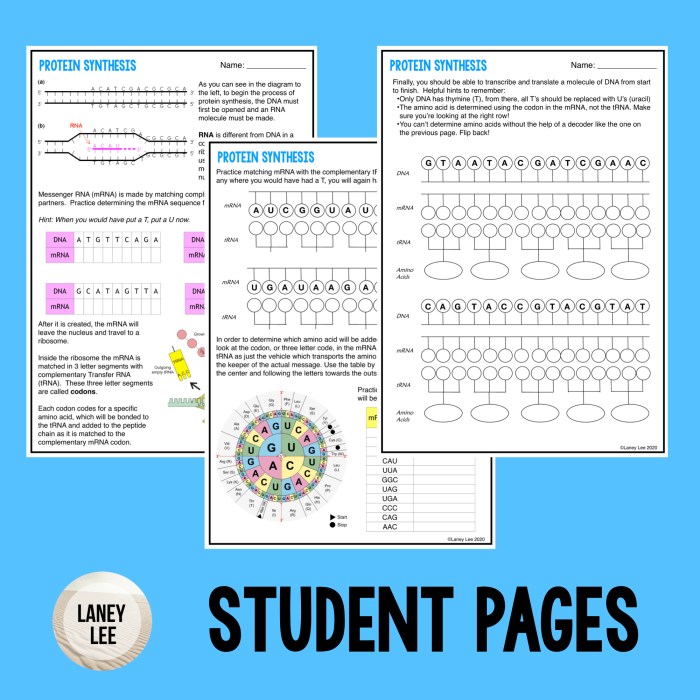
Overview of Protein Synthesis

Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins. Proteins are essential for life, as they perform a wide range of functions, including structural support, metabolism, and cell signaling.
The central dogma of molecular biology states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. DNA contains the instructions for making proteins, and RNA carries these instructions to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
Transcription, Answer key to protein synthesis worksheet
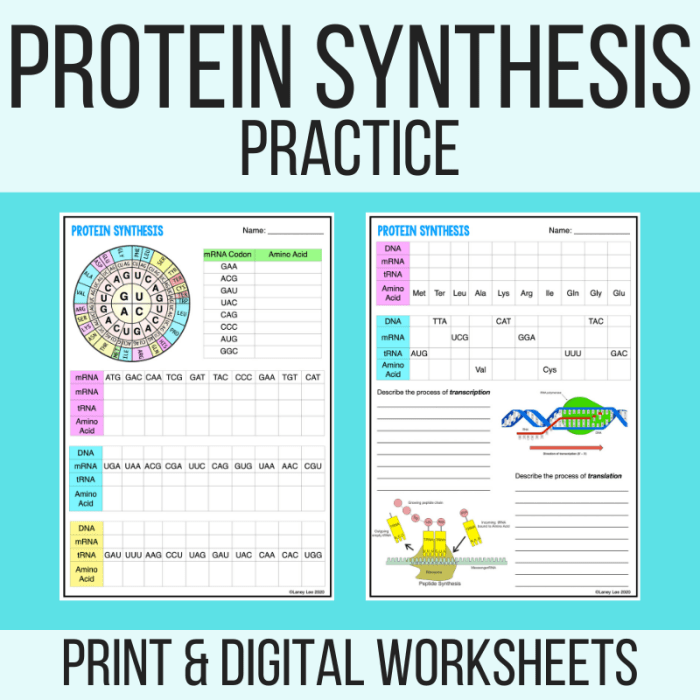
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into RNA. This process is carried out by RNA polymerase, an enzyme that binds to the DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule.
The RNA molecule that is produced by transcription is called messenger RNA (mRNA). mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
Translation
Translation is the process of converting the genetic information in mRNA into a protein. This process is carried out by the ribosome, a large complex of RNA and protein molecules.
The ribosome binds to the mRNA and reads the genetic information in the mRNA. The ribosome then uses this information to assemble a chain of amino acids, which form the protein.
Genetic Code
The genetic code is a set of rules that specify how the genetic information in mRNA is translated into a protein. The genetic code is composed of codons, which are three-nucleotide sequences that code for specific amino acids.
There are 20 different amino acids, and each amino acid is coded for by one or more codons. The genetic code is universal, meaning that it is the same in all living organisms.
Mutations
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental factors, such as radiation, and errors in DNA replication.
Mutations can have a variety of effects on protein synthesis. Some mutations can lead to the production of non-functional proteins, while others can lead to the production of proteins that are not functional.
Applications of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is used in a variety of applications in biotechnology. One of the most important applications of protein synthesis is the production of therapeutic proteins.
Therapeutic proteins are proteins that are used to treat a variety of diseases. These proteins can be produced using recombinant DNA technology, which involves inserting the gene for the protein into a host cell and then culturing the host cell to produce the protein.
Query Resolution: Answer Key To Protein Synthesis Worksheet
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
How does transcription occur?
Transcription involves the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.