Embark on an exploration of the styloid process of the foot, a captivating anatomical structure that plays a pivotal role in foot mechanics and weight-bearing. Delve into its intricate structure, clinical significance, and the diverse treatment options available for styloid process-related conditions.
Unveiling the anatomical intricacies of the styloid process, we discover its bony landmarks and surrounding structures, gaining insights into its functional significance in supporting the foot’s complex biomechanics.
Styloid Process of the Foot: An Overview
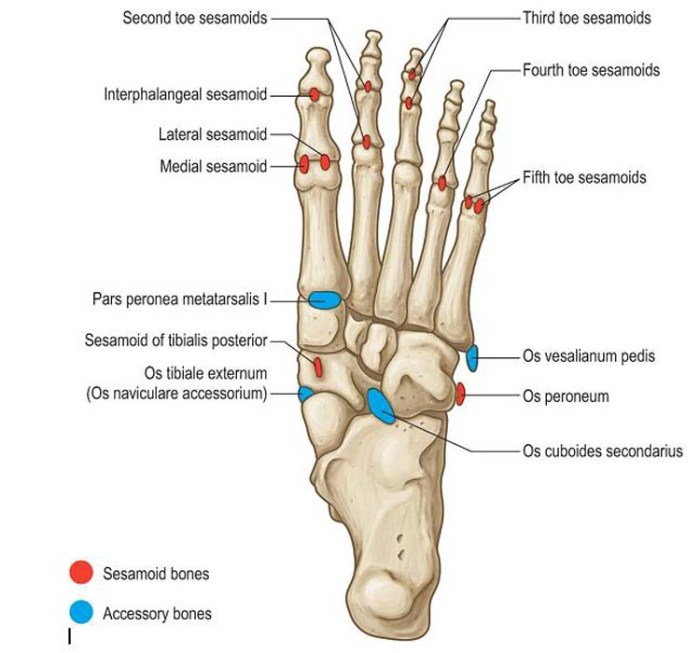
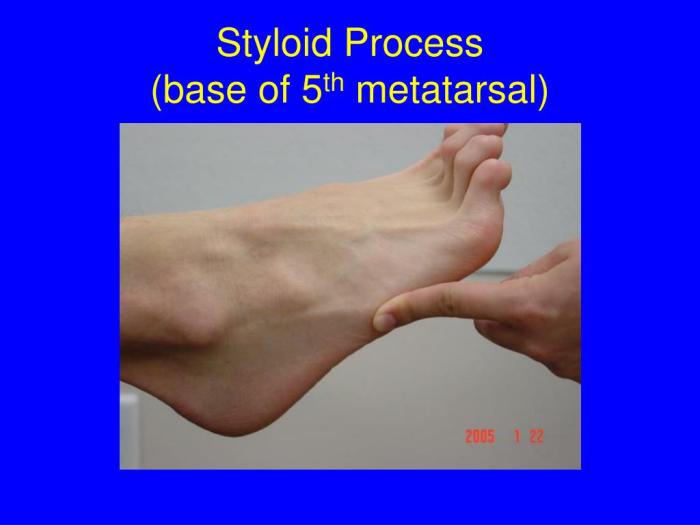
The styloid process of the foot is a small, bony projection located on the medial side of the calcaneus, the heel bone. It is a prominent landmark that serves as an attachment point for several ligaments and tendons, and plays a crucial role in foot mechanics and weight-bearing.
Anatomical Location and Structure
The styloid process is located at the inferior aspect of the calcaneus, just below the sustentaculum tali. It projects medially and slightly posteriorly, forming a small, hook-like structure. The styloid process is composed of cortical bone, which is the dense, outer layer of bone that provides strength and rigidity.
Bony Landmarks and Surrounding Structures
The styloid process is surrounded by several important bony landmarks and structures. Anteriorly, it is adjacent to the plantar fascia, a thick band of connective tissue that runs along the sole of the foot and supports the arch. Posteriorly, it is located near the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Medially, the styloid process is bordered by the flexor retinaculum, a ligament that holds the flexor tendons in place as they pass through the ankle joint.
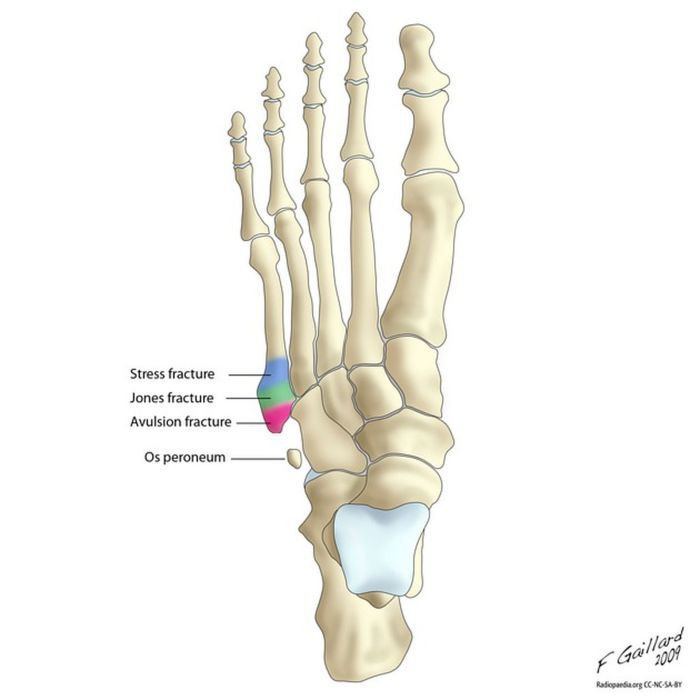
The styloid process of the foot, a bony projection at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, plays a crucial role in maintaining the arch of the foot. Its name, derived from the Greek word “stylos” meaning “pillar,” aptly describes its function.
Intriguingly, the acronym KSAO is sometimes used in medical contexts. Curious about its meaning? You can find a comprehensive explanation at what does ksao stand for . Returning to the styloid process of the foot, its proper alignment and stability are essential for optimal foot mechanics and preventing various foot disorders.
Role in Foot Mechanics and Weight-Bearing
The styloid process plays a significant role in foot mechanics and weight-bearing. It provides an attachment point for the plantar fascia, which helps to maintain the arch of the foot and absorb shock during walking and running. Additionally, the styloid process serves as an insertion point for the flexor hallucis longus tendon, which is responsible for flexing the big toe.
By anchoring these structures, the styloid process helps to stabilize the foot and facilitate proper movement.
Clinical Significance of the Styloid Process: Styloid Process Of The Foot
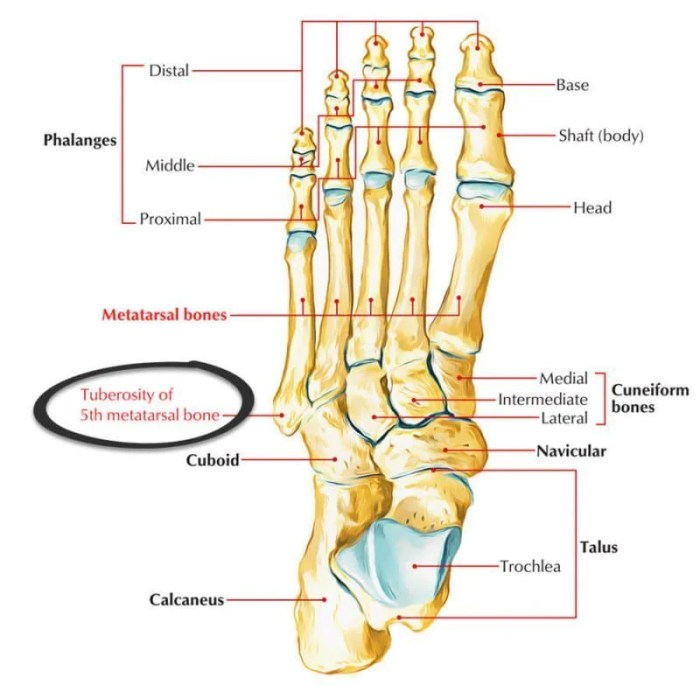
The styloid process, a bony prominence on the heel bone, plays a crucial role in foot mechanics and is often associated with various clinical conditions.
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spurs, Styloid process of the foot
Plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the plantar fascia ligament, is commonly linked to the styloid process. The ligament, which runs along the sole of the foot, attaches to the styloid process and can become irritated or inflamed due to excessive stress or strain.
Heel spurs, bony growths that develop on the underside of the heel bone, can also contribute to plantar fasciitis by putting pressure on the plantar fascia.
Both plantar fasciitis and heel spurs cause pain and discomfort in the heel, particularly when walking or standing. They can significantly impact foot function and mobility.
Diagnostic Techniques
To diagnose styloid process-related issues, healthcare professionals typically perform a physical examination of the foot and ankle. They may also order imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to visualize the styloid process and surrounding structures. These tests can help identify any abnormalities, such as inflammation, bone spurs, or other underlying conditions.
Surgical Management of Styloid Process Disorders
Surgical intervention may be necessary to address persistent or severe styloid process-related conditions. The choice of surgical procedure depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors.
Percutaneous Styloidectomy
Percutaneous styloidectomy involves the removal of the styloid process through a small incision in the skin. This minimally invasive technique is typically performed under local anesthesia and uses a specialized needle or drill to access and remove the affected bone.
Percutaneous styloidectomy is often used for isolated styloid process elongation or hypertrophy.
Open Styloidectomy
Open styloidectomy is a more extensive surgical procedure that involves a larger incision and direct visualization of the styloid process. It is typically performed under general anesthesia and allows for a more precise removal of the affected bone, including any surrounding soft tissue attachments.
Open styloidectomy may be necessary for complex cases, such as those involving anatomical variations or concurrent nerve entrapment.
Potential Risks and Complications
Surgical management of styloid process disorders carries potential risks and complications, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve damage
- Recurrence of symptoms
- Scarring
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation
After surgery, patients typically require a period of rest and immobilization to promote healing. Post-operative care includes pain management, wound care, and gradual rehabilitation exercises. Physical therapy may be recommended to restore range of motion and strength in the affected area.
The duration of rehabilitation varies depending on the extent of surgery and individual recovery.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options aim to alleviate pain and improve function without resorting to surgery. These non-surgical interventions focus on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and restoring normal biomechanics.
The effectiveness of conservative treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their adherence to the treatment plan.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing styloid process-related conditions. It involves exercises that strengthen the muscles surrounding the foot and ankle, improve range of motion, and correct biomechanical imbalances.
Specific exercises may include:
- Calf stretches
- Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion exercises
- Heel cord stretching
- Balance and proprioception exercises
Orthotics
Custom-made orthotics can help correct abnormal foot biomechanics and reduce stress on the styloid process. They can be designed to provide support, cushioning, and alignment, thus reducing pain and improving function.
Orthotics may be particularly beneficial for patients with flat feet or high arches, as these conditions can contribute to styloid process pain.
Other Conservative Measures
Other conservative measures that may be recommended include:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice packs to reduce inflammation
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain
FAQ Summary
What is the styloid process of the foot?
The styloid process is a bony projection located on the heel bone (calcaneus) that serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles, contributing to foot stability and movement.
What are the common conditions associated with the styloid process?
Plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, and Achilles tendinitis are common conditions that can involve the styloid process, causing pain and inflammation in the heel and arch of the foot.
How is the styloid process treated?
Treatment options range from conservative measures such as rest, ice, and physical therapy to surgical interventions in severe cases. The specific treatment approach depends on the underlying condition and its severity.